
Thoracic Radiculopathy: Overview, Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
What is Thoracic Radiculopathy?
Thoracic radiculopathy is when an irritation or compression of a nerve root occurs in the thoracic region of the spine, the middle section of the back. The thoracic spine consists of twelve vertebrae (T1-T12) located between the cervical (neck) and lumbar (lower back) regions. When a nerve root in this area becomes compressed or inflamed, it can cause pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness along the path of the affected nerve. While this condition is relatively rare, it can still cause significant discomfort and functional impairment.
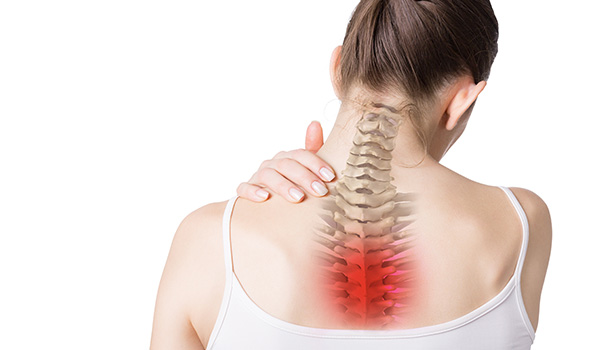
Symptoms of Thoracic Radiculopathy
Symptoms vary depending on the affected nerve root. Common symptoms include:
- Localized Pain: Pain felt along the middle or upper back, often following the path of the affected nerve, it can be sharp, burning, or stabbing in nature.
- Radiating Pain: The pain can radiate along the ribcage, into the chest, abdomen, or back, potentially mimicking conditions related to the heart. This radiating pain typically follows a specific dermatome or area of the skin supplied by a single nerve.
- Numbness and Tingling: Sensations of numbness or tingling, commonly referred to as "pins and needles," felt along the skin corresponding to the affected nerve.
- Muscle Weakness: Weakness may develop in muscles controlled by the affected nerve, which can interfere with one’s daily activities and routine.
- Sensory Changes: In addition to numbness and tingling, there may be altered sensation in the areas supplied by the affected nerve root.
- Difficulty with Movement: Some individuals may experience difficulty with movement due to pain, weakness, or discomfort in the upper back and ribs.
Causes of Thoracic Radiculopathy
Thoracic radiculopathy can be caused by several factors that lead to compression or irritation of the thoracic nerve roots. These include:
- Herniated Disc: A herniated disc in the thoracic spine can press against the nearby nerve roots. While this is more common in the cervical and lumbar regions, it can occur in the thoracic spine as well.
- Spinal Stenosis: Spinal stenosis refers to a narrowing of the spinal canal, which can place pressure on the nerve roots. In the thoracic spine, stenosis may be caused by age-related degeneration or structural abnormalities.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: As the discs between the vertebrae in the spine age, they can lose their cushioning ability, leading to disc bulging or herniation and compression of the nerve roots.
- Trauma or Injury: Any traumatic injury to the spine, such as a fracture, whiplash, or direct impact, can damage the thoracic nerve roots, causing radiculopathy.
- Spondylosis: This refers to age-related wear and tear of the vertebrae and discs, leading to bone spurs (osteophytes) that can impinge on the nerve roots.
- Tumors or Infections: Although less common, tumors, infections, or abscesses within the thoracic spine can cause compression of the nerve roots and lead to radiculopathy.
- Post-Surgical Changes: Surgical procedures on the spine can occasionally lead to scar tissue or other changes that compress the nerve roots, resulting in radiculopathy.
- Other Medical Conditions: Conditions like diabetes or autoimmune disorders (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis) can increase the risk of nerve damage, contributing to radiculopathy.
Treatment for Thoracic Radiculopathy
Treatment for thoracic radiculopathy depends on the severity of symptoms, the underlying cause, and the overall health of the patient. In many cases, a combination of conservative treatments and, in some cases, more invasive interventions can be effective. Treatment options include:
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises and stretches to strengthen the muscles supporting the thoracic spine, improve posture, and reduce nerve compression, a physical therapist also employs techniques like manual therapy, modalities (e.g., heat, ice, ultrasound), and ergonomic advice.
- Medications: Medications for pain and inflammation such as anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen, oral steroids, in more severe cases, nerve pain medications like gabapentin, and pregabalin.
- Epidural Steroid Injections: An injection of corticosteroids around the spinal cord can reduce inflammation and relieve nerve pain, especially in the case of herniated discs or spinal stenosis.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold to the affected area can help alleviate pain and muscle spasms. Heat can improve circulation and relax muscles, while cold can reduce swelling and numb the pain.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Avoiding activities such as heavy lifting or twisting motions, which can exacerbate the pain. Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and incorporating gentle exercises can also promote long-term spinal health.
- Surgical Treatment: Surgery may become necessary in the case of persistent symptoms or significant nerve damage. Common surgeries include discectomy (removal of herniated disc material), laminectomy (removal of vertebral bone to relieve nerve compression), spinal fusion (stabilization of the spine), and foraminotomy (widening of the foramen to relieve pressure on nerve roots).
Prognosis
With appropriate treatment, most cases of thoracic radiculopathy improve over time. While conservative treatments like physical therapy and medication can relieve symptoms for many patients, more severe or persistent cases may require surgical intervention. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing the condition effectively and minimizing the risk of permanent nerve damage.
If you are experiencing symptoms of thoracic radiculopathy, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Reach out to us
If you're ready to take the next step toward better health, visit the North Florida Medical Center's locations page to find the most convenient center near you. You can also contact the team directly for more information or request an appointment online to start your personalized care journey today.
Our locations Contact us Request appointment